License Plate Recognition using
Artificial Neural Network
Training the model
The Artificial Neural Network is implemented using the platform Tensorflow with Tensorflow 2 Object Detection API.
Model Training is a fundamental part in Machine Learning, because at the end the goal is to obtain a network that generalize well with new data at the input. In this case, around 400 photos of license plate have been used for training the model.
Then, the trained model was exported to be used as an automatic license plate recognition function (with never seen input data) in the main program.
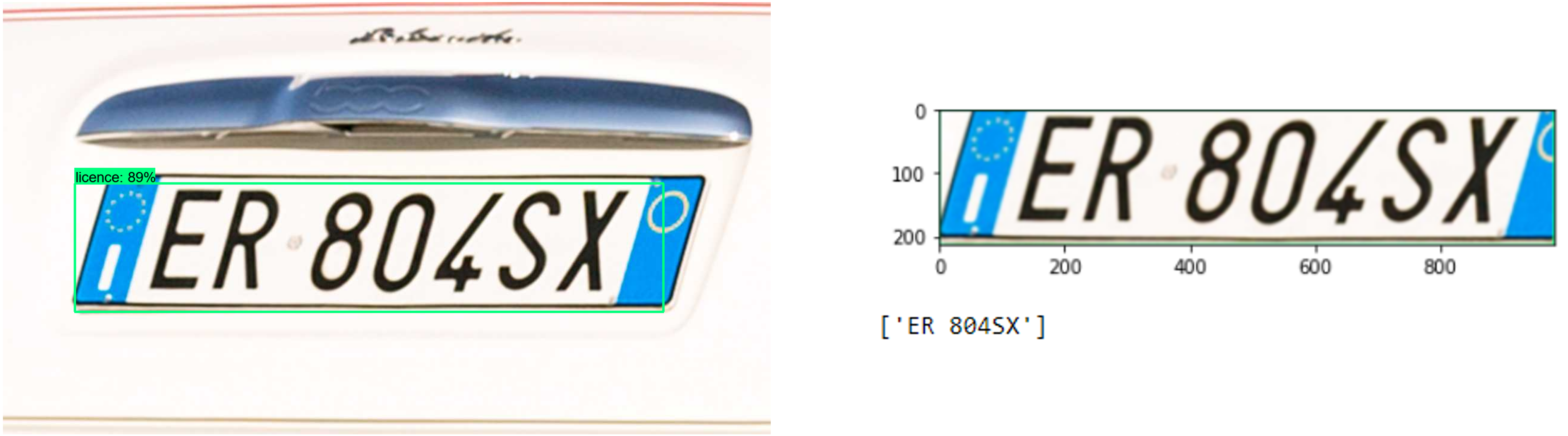
To extract the correct ROI (Region Of Interest) and the number of the license plate it was used the Python's package EasyOCR. At the end, with this module the program will extract the number of the plate from a photo taken by a speed camera, that will be used in the next steps for comparing it with the packets sent from the clients.
Client-Server communication
Cars and speed camera communication
The Client-Server communication has been implemented using the Python's library Socket.io which provides simple methods for develop the connection. When the server is started, it waits for a client to connect. Once a client connects itself to the server it sends to it a packet containing the plate number and the license number of the driver, both properly encrypted, and a secret unique ID which is stored inside the driver license chip and is needed to select the correct key for the decryption of the data. The client, then, waits for the server's acknowledgement reply before disconnecting.
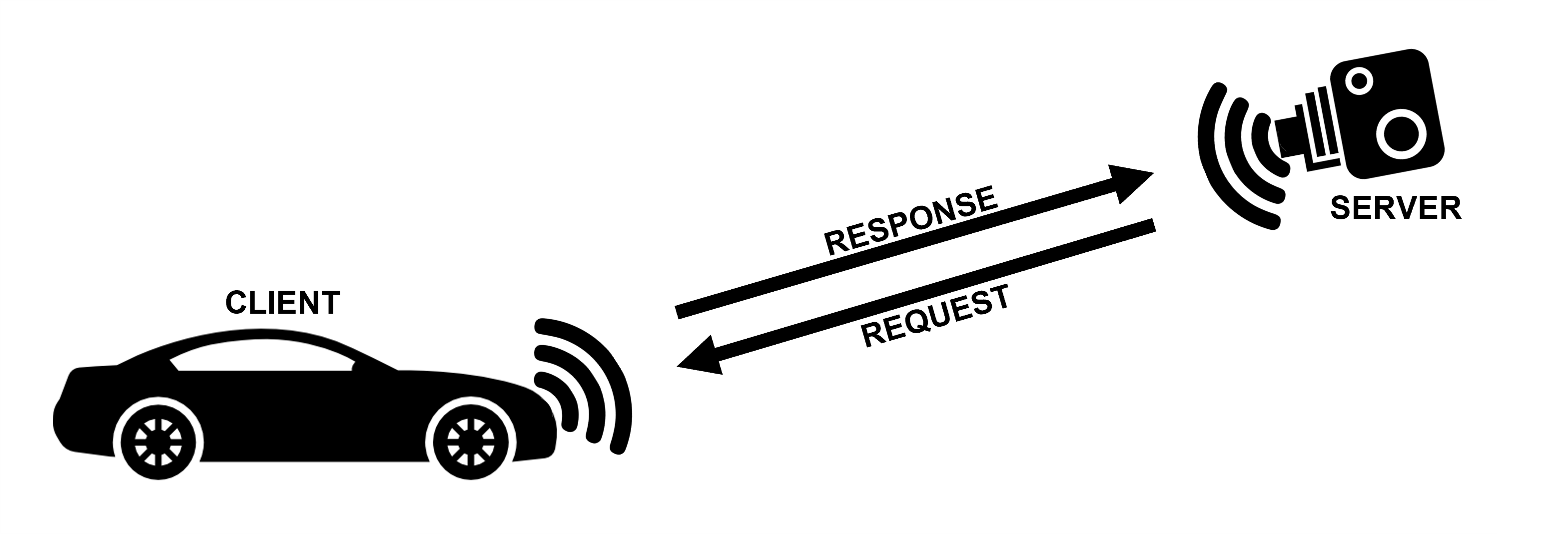
The server stores all the packets received from the clients in a Python's dictionary with the secret unique ID as key.
When an infringement is committed the server starts a new thread for the recognition of the driver while the main process continues to accept new clients. The recognition thread decrypts all the packets received and performs the analysis of the photo in order to obtain the plate number of the trasgressor. Then it selects the license number of the transgressor comparing the plate number obtained from the photo with the ones stored in the dictionary. It than retrieve all the driver information from the police database and display them in a graphic interface.
Security and Cryptography
RSA encryption, nonce and hash function
The communication between clients and server is secured against multiple types of attacks.
First, all the data are encrypted using an RSA encryption algorithm where the keys are generated from two 2048bit prime numbers, so data are secured against sniffing and spoofing attacks.
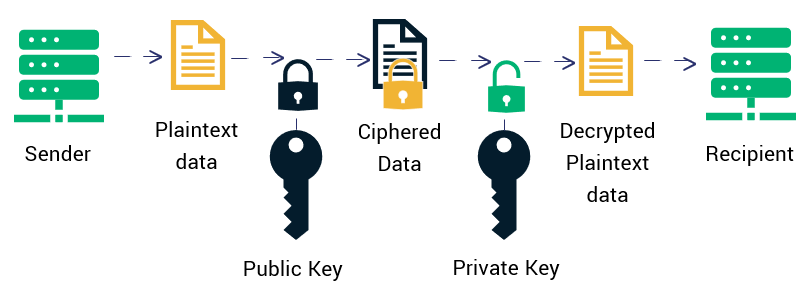
The two keys are linked by a secret unique ID stored both on the license and in the police database.
To avoid reply attacks, when a client connects, the server provides a randomly generated nonce and a timestamp that the client must attach to the packet. When the packet is decrypted the nonce is compared with the one originally generated, so an old reply cannot be reused.
Last but not least, to guarantee the integrity of the message arrived at the server an hash function is computed on the data and the nonce before the encryption (a SHA256 algorithm has been used).
It is also verified that the client's data (plate and license number) matches with a standard pattern.
Below an example of a client's packet before encryption.
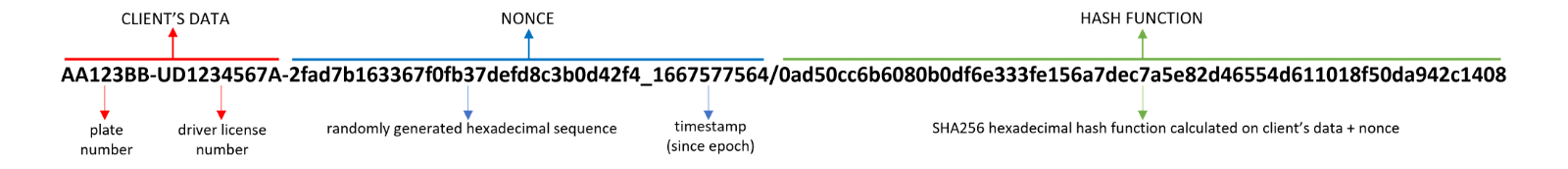
All the security algorithms are implemented using the packages PyCryptodome and Secrets.
Visualization of Driver's Details
GUI implementation
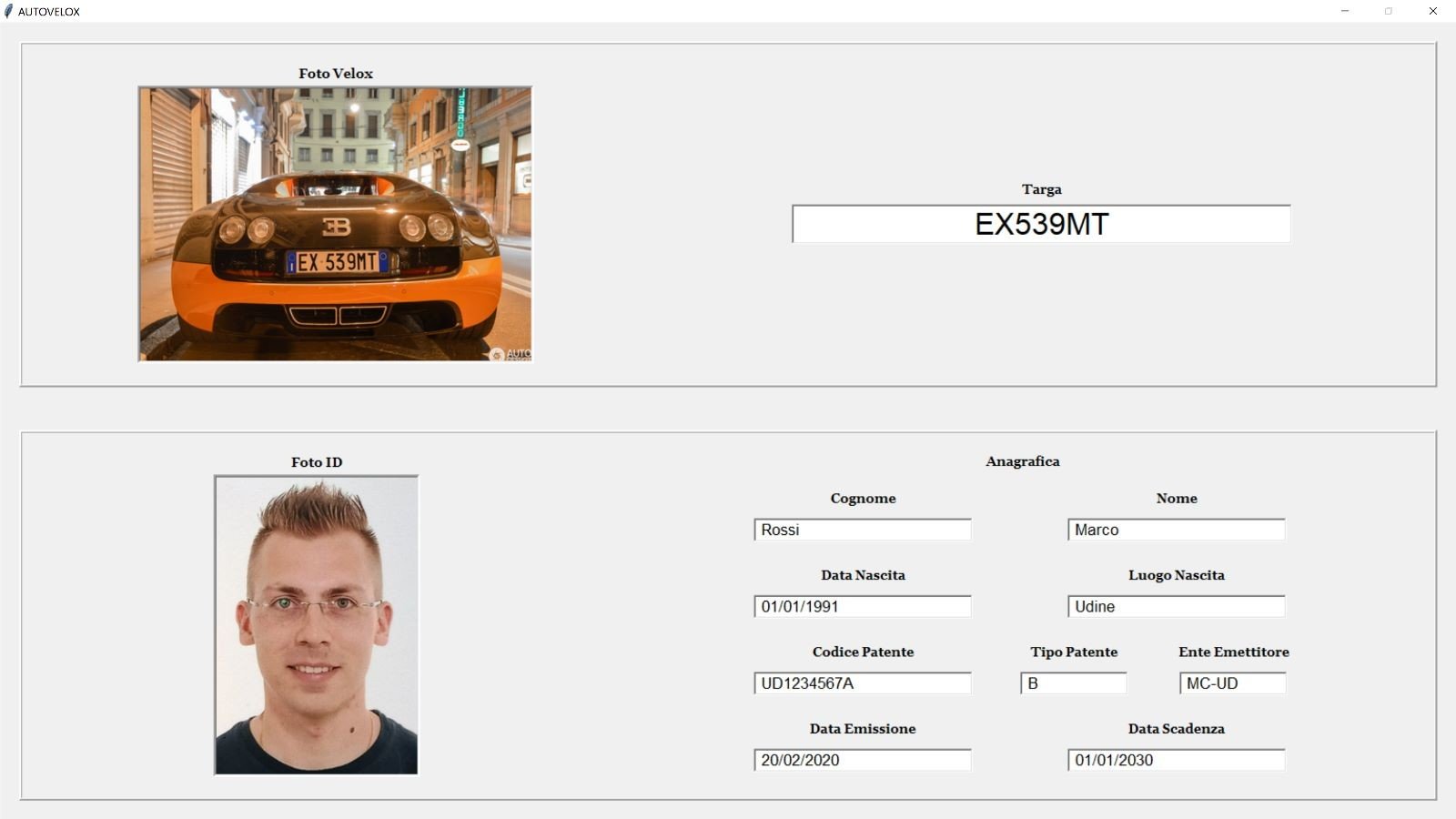
All the data about the car and the offending driver are shown in a graphic interface implemented using Tkinter, a cross platform GUI toolkit that comes native in Python.
The upper half of the window shows the data received from the smart speed camera, the photo of the car that committed the infringement and the plate number extracted using the neural network.
In the other half of the window are shown all the driver data retrieved from the police database, from photo and license code to name and date of birth.